Submit feedback
How do you determine the appropriate cable length and capacity for a given cable reel?
 2024.09.04
2024.09.04
 Industry News
Industry News
Determining the appropriate cable length and capacity for a given cable reel involves several steps. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
Identify the Application Requirements
Voltage and Current Rating: Determine the voltage and current requirements of the equipment that the cable will power.
Cable Type: Identify the type of cable needed based on the application (e.g., power, data, control).
Environmental Conditions: Consider the environment where the cable will be used (indoor, outdoor, temperature fluctuations, exposure to chemicals, etc.).
Calculate the Desired Cable Length
Distance to Equipment: Measure the distance from the power source to the equipment. Include any additional length for routing and potential obstacles.
Cable Routing: Consider how the cable will be routed. Will it need to go around corners or through walls? This can add to the required length.
Future Needs: If you anticipate needing to move equipment or add additional devices in the future, consider adding extra length.
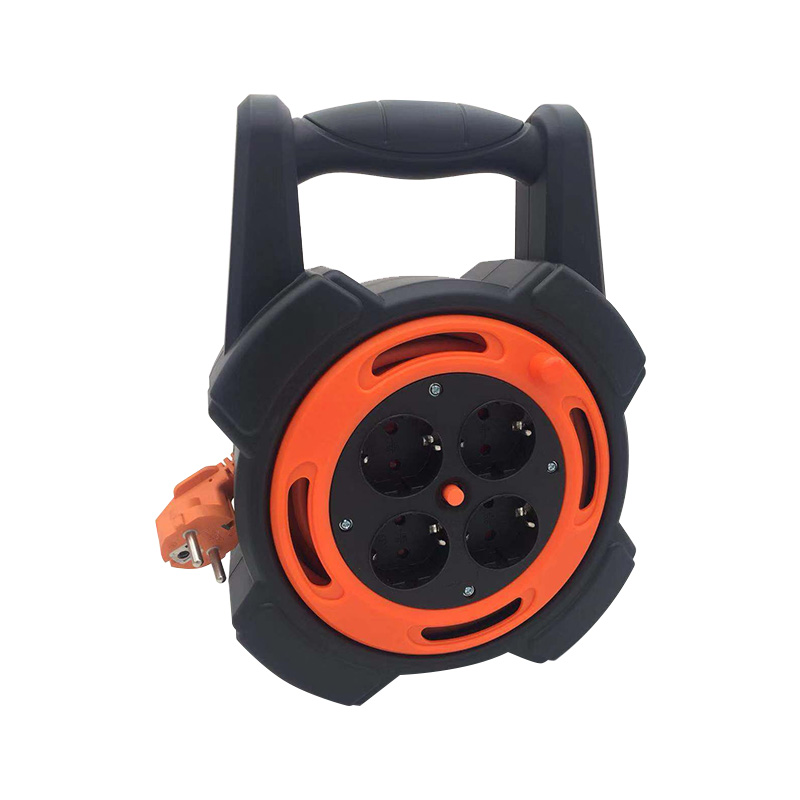
Determine the Reel Capacity
Reel Size: Check the specifications of the cable reel. Each reel has a maximum cable capacity, often listed in meters or feet, and may have a maximum weight limit.
Cable Diameter: Measure the diameter of the cable you are using. The total length of cable that can fit on the reel will depend on the diameter of the cable. Use the formula for the circumference of a circle (C = πD) to calculate the space needed for one loop of cable on the reel.
Wind Layers: Consider how many layers of cable will be wound on the reel. More layers will require more space, reducing the total length of cable that can fit.

Consider Electrical Specifications
Voltage Drop: For longer cable runs, calculate the voltage drop. Longer cables can lead to a significant voltage drop, which can affect equipment performance.
Current Capacity: Ensure that the cable can handle the required current without overheating. Refer to standard charts that list the ampacity of various cable sizes.
Finalize the Specifications
Safety Margin: Always include a safety margin in your calculations. This can be an additional percentage (e.g., 10-20%) added to your length or current capacity to account for unexpected needs or conditions.
Consult Standards: Refer to industry standards and guidelines (like NEC in the US) for additional specifications on cable types, lengths, and capacities.
Practical Examples
Example 1: If you need to power a piece of equipment 50 meters away, and the cable has a diameter of 10 mm, you might check if the reel can hold at least 60 meters of cable, allowing for routing and extra length.
Example 2: For a current of 20 A, ensure the selected cable size can handle that load without exceeding the ampacity, and check for voltage drop if the length is beyond recommended limits.
By following these steps, you can determine the appropriate cable length and capacity for a given cable reel. Always remember to factor in future needs, environmental conditions, and safety margins to ensure optimal performance and safety in your electrical installations.
 TOP
TOP
 ENG
ENG
 English
English русский
русский 한국어
한국어 Deutsch
Deutsch