Submit feedback
How is the heat resistance of polypropene PP power strip under high load conditions?
 2025.02.13
2025.02.13
 Industry News
Industry News
Polypropylene (PP) is a commonly used thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, electrical insulation and mechanical properties. However, its heat resistance needs to be carefully evaluated under high load conditions, especially when used to manufacture electrical devices such as power sockets or polypropene pp power strips.
Basic heat resistance properties of polypropylene
Melting point: The melting point of PP is usually between 160°C and 170°C.
Heat deformation temperature: The heat deformation temperature (HDT) of ordinary PP is about 80°C to 100°C (under 0.45 MPa load). If glass fiber or other reinforcement materials are added, its heat deformation temperature can be increased to 120°C or higher.
Long-term use temperature: The long-term use temperature of PP without external force is generally 80°C to 100°C, but its heat resistance will drop significantly under high load conditions.
Performance under high load conditions
When PP materials are used in power sockets or strips, they may face the following situations:
Heat problem: Under high load conditions (such as multiple high-power electrical appliances working at the same time), the conductors inside the strip will generate heat, causing local temperature rise.
Heat aging: If the temperature exceeds the long-term use temperature range of PP (such as over 100°C), PP may undergo heat aging, which is manifested as brittle material, reduced strength, or even deformation.
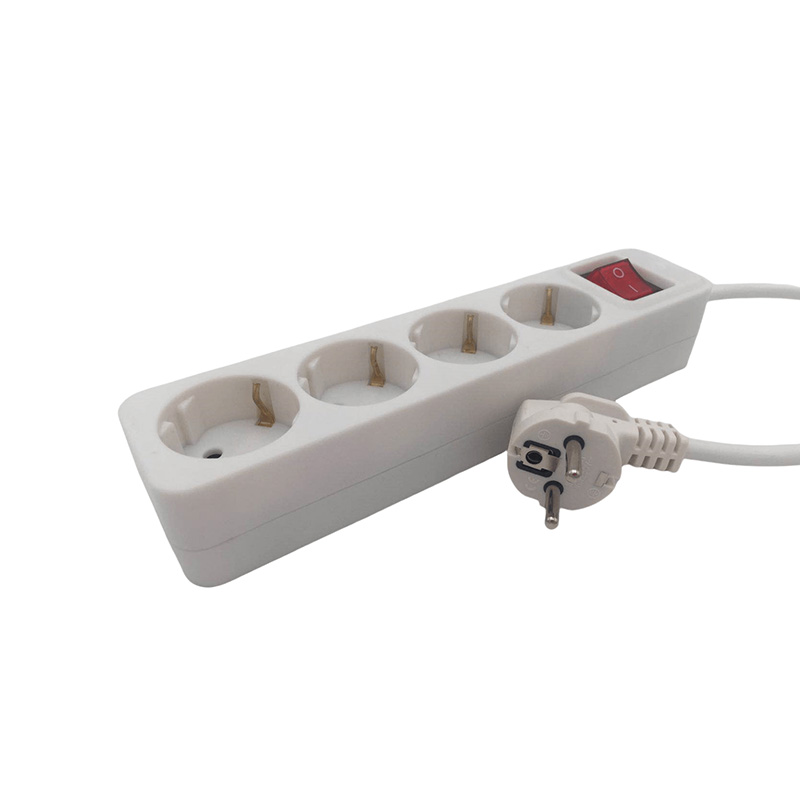

Softening and deformation risk: If the temperature is close to the heat deformation temperature of PP (80°C-100°C), the material may soften, affecting the structural integrity of the strip.
Methods to improve heat resistance
In order to improve the heat resistance of PP under high load conditions, the following measures can be taken:
Modified PP material: The heat deformation temperature and mechanical strength of PP can be significantly improved by adding glass fiber, mineral fillers or heat-resistant additives.
Flame retardant addition: In electrical equipment, PP usually needs to be added with flame retardants to meet safety standards (such as UL94 V-0). Some flame retardants can also indirectly improve the heat resistance of materials.
Design optimization: Reduce heat accumulation by optimizing the design of the plug strip. For example, add heat dissipation holes, use thicker wires, or choose better conductor materials (such as copper instead of aluminum).
Alternative materials: For high-load applications, consider using engineering plastics with higher heat resistance, such as PA (nylon), PC (polycarbonate) or PBT (polybutylene terephthalate).
Precautions in practical applications
Rated power limit: Make sure the design of the plug strip meets the rated power requirements and avoid long-term overload operation.
Ambient temperature control: Avoid placing the plug strip in a high-temperature environment (such as direct sunlight or near a heat source).
Certification standards: Choose plug strip products that meet international or national standards (such as UL, CE, CCC), which are usually subject to rigorous heat resistance and safety tests.
Ordinary PP materials may soften or thermally age due to increased temperature under high load conditions, so their heat resistance may not be sufficient to meet the needs of high-load plug strips. By modifying PP or choosing other materials with higher heat resistance, the reliability and safety of the product can be effectively improved. In practical applications, it is recommended to strictly abide by the rated power limit and choose certified high-quality products to ensure safety.
 TOP
TOP
 ENG
ENG
 English
English русский
русский 한국어
한국어 Deutsch
Deutsch