Submit feedback
How to design the CABLE REEL to ensure that the cable is not damaged during the retraction process?
 2025.02.20
2025.02.20
 Industry News
Industry News
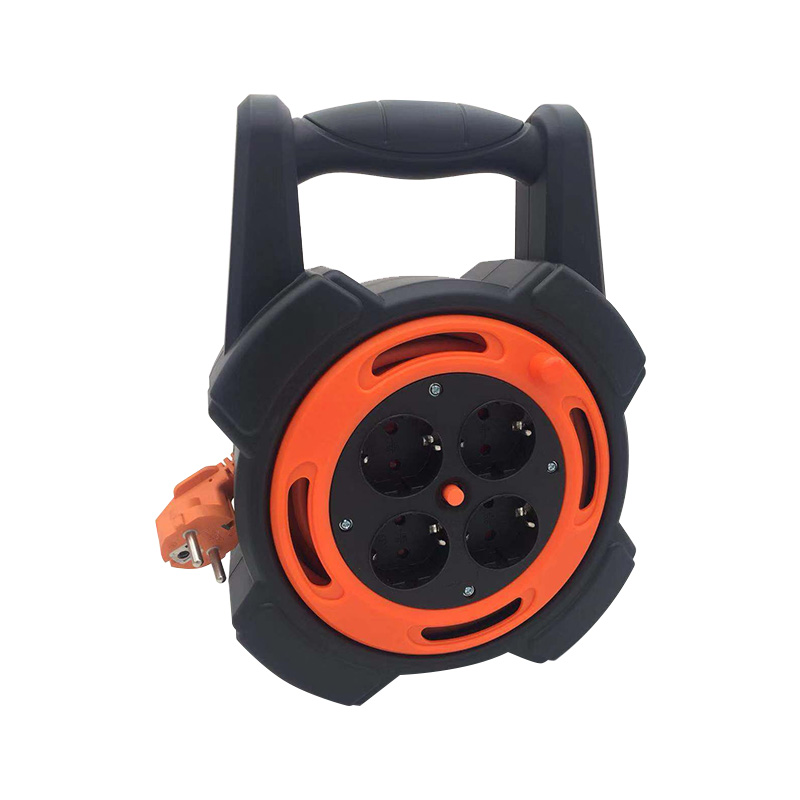
Designing a CABLE REEL to ensure that the cable is not damaged during the reeling process requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors such as mechanical structure, material selection, operation mode, and environmental adaptability. The following are detailed design principles and methods:
Reasonably select the material of the cable reel
Durability and strength: The frame and shaft of the reel should be made of high-strength materials (such as aluminum alloy, stainless steel or engineering plastics) to withstand the weight and tension of the cable.
Corrosion resistance: When used in a humid or dusty environment, choosing corrosion-resistant materials (such as galvanized steel or stainless steel) can extend the life of the reel.
Lightweight design: For portable cable reels, lightweight but strong materials (such as carbon fiber composites) are preferred to reduce the overall weight.
Optimize the geometry of the reel
Winding diameter and spacing: According to the diameter and bending radius of the cable, design a suitable winding diameter and interlayer spacing to avoid excessive bending or squeezing of the cable.
Note: The minimum bending radius of the cable is usually determined by its specifications. Too small a bending radius may cause damage to the insulation layer or breakage of the internal conductor.
Separator: In the multi-layer winding design, separators or guide grooves are added to prevent friction or misalignment between cable layers.
Center hole design: Make sure the center hole of the reel is large enough to facilitate the installation of the shaft or other fixing device, while reducing the pressure on the cable.
Control the tension of the cable
Constant tension system: Constant tension control is achieved through springs, motors or hydraulic devices to ensure that the cable always maintains the appropriate tightness during the reeling process.

Function: Prevent the cable from stretching and deforming due to excessive tension, or loose winding due to insufficient tension.
Intelligent adjustment function: In high-end cable reels, sensors and control systems can be added to monitor the cable tension in real time and adjust it automatically.
Protect the surface of the cable
Smooth lining: Add a smooth protective layer (such as polyurethane coating or Teflon material) to the inside of the reel to reduce friction between the cable and the reel.
Anti-slip design: Add a slight texture or elastic pad to the contact surface to prevent the cable from sliding or shifting, while avoiding scratching the cable sheath.
Flexible buffer: Install flexible guides at key locations (such as entrances and exits) to guide the cable in and out of the reel smoothly and avoid damage caused by sharp edges.
Improved retraction mechanism
Manual vs. automatic:
Manual reel: Design a handle or rocker that is easy to operate and ensure smooth rotation.
Automatic reel: Use an efficient motor drive system combined with a reducer and clutch to ensure smooth cable retraction.
Speed control: Set an adjustable speed function to avoid twisting or tangling of the cable due to excessive retraction.
Overload protection: Add overload protection devices (such as fuses or limit switches) to prevent damage to the motor or mechanical parts due to overload.
Enhance environmental adaptability
Waterproof and dustproof: When used outdoors or in harsh environments, design a sealed structure to prevent moisture or dust from entering the reel.
Temperature adaptability: Choose materials that are resistant to high or low temperatures, and ensure that the cable reel can still work normally under extreme temperatures.
UV resistance: For reels exposed to sunlight for a long time, choose materials with UV-resistant coating to prevent aging.
Regular maintenance and inspection
Lubrication system: Provide good lubrication for moving parts such as shafts and gears, reduce wear and extend service life.
Easy to disassemble design: Design modular structure to facilitate users to clean, inspect and repair.
Marking and instructions: Mark the maximum load capacity of the cable, recommended reeling speed and other information on the reel to help users operate correctly.
Designing a cable reel to ensure that the cable is not damaged during the reeling process requires comprehensive consideration of multiple aspects such as material selection, structural design, tension control and environmental adaptability. By optimizing the geometry of the reel, introducing a constant tension system and enhancing protection measures, the safety and service life of the cable can be significantly improved. In addition, with the advancement of technology, the addition of intelligent functions will further enhance the performance and user experience of the cable reel.
 TOP
TOP
 ENG
ENG
 English
English русский
русский 한국어
한국어 Deutsch
Deutsch